| |
|
Location and Monitoring Service (LMS)
|
The Location and Monitoring Service (LMS) is a locationing technology optimized for use in urban environments and in buildings, where other technologies, such as GPS, may not work well or at all.
Two different types of LMS are defined: Multilateration LMS (M-LMS) and non-multilateration LMS. The respective FCC definitions are:
Multilateration LMS system: A system that is designed to locate vehicles or other objects by measuring the difference of time of arrival, or difference in phase, of signals transmitted from a unit to a number of fixed points or from a number of fixed points to the unit to be located.
Non-multilateration LMS System. A system that employs any of a number of non-multilateration technologies to transmit information to and/or from vehicular units.
LMS shares the band with a variety of users. Most prominently, the band is used by a multitude of unlicensed devices such as many models of cordless phones, baby monitors, and wireless speakers.
LMS licenses were first auctioned in 1999, in FCC auction 21, and in a follow-up auction (39) in 2001. Since then, much effort has been spent creating frameworks and operational constraints that allow LMS, unlicensed devices, and other services to share the band. (See the CommLawBlog link for more details). The FCC has created a chart that shows the hierarchy of rights in this band. The chart has been uploaded under the "FCC Proceedings" heading below.
The majority of licenses in the LMS auctions were won by Progeny LLC. Some of the other winners have since defaulted on their bid payments. Progeny received a waiver of the FCC rules to allow its multilateration system to locate objects other than vehicles. It also received a waiver to provide locationing service by using one-way transmissions from a low density of powerful sites, rather than by using two-way technology that was originally envisioned for LMS.
The 902-928 MHz band has been divided into LMS blocks, which are then authorized for M-LMS or non-multilateration LMS, or shared between the two. LMS operates under Subpart M of Part 90 of the FCC rules, and is considered part of the Intelligent Transportation Systems Radio Service.
In the range 902-927.25 MHz, LMS systems are limited to 30 W ERP. In the range 927.25-928 MHz, the power limit is 300 W ERP [47 CFR 90.205(l)].
|
Frequency Bands |
| Band | Use | Service11 | Table |
| 902 - 904 MHz | Non-multilateration LMS | - | N |
| 904 - 909.75 MHz | Multilateration LMS Block A | - | N |
| 909.75 - 921.75 MHz | Non-multilateration LMS (919.75-921.75 shared with multilateration LMS) | - | N |
| 919.75 - 921.75 MHz | Multilateration LMS Block B (shared with non-multilateration LMS) | - | N |
| 921.75 - 927.75 MHz | Multilateration LMS Block C | - | N |
| 927.25 - 927.5 MHz | Multilateration LMS Block C (forward link) | - | N |
| 927.5 - 927.75 MHz | Multilateration LMS Block B (forward link) | - | N |
| 927.75 - 928 MHz | Multilateration LMS Block A (forward link) | - | N |
Associated Files:
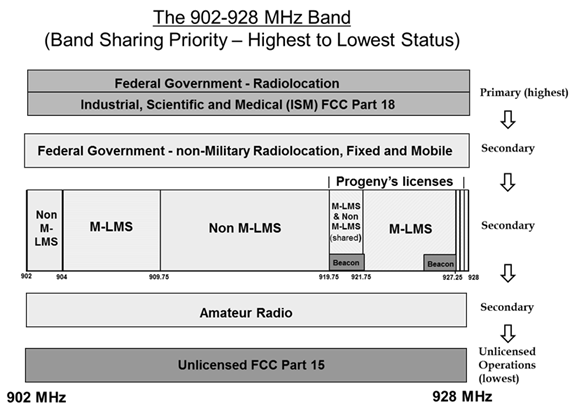
Hierarchy of rights in the 902-928 MHz band (from FCC 13-78).
|
|
|
|
|